IV Therapy: Future, Supervision & Best Practices [2024]
Is intravenous (IV) therapy merely a medical procedure, or is it a cornerstone of modern healthcare, poised to reshape patient care as we know it? The landscape of medicine is being fundamentally altered by advancements in IV therapy, with implications that span patient safety, treatment efficacy, and the very structure of medical practice.
The administration of fluids, medications, blood products, and nutrients directly into a patient's bloodstream via a vein has become a standard practice across diverse medical settings. Yet, the simplicity of this description belies the complex evolution and future trajectory of this critical therapeutic modality. The evolution of IV therapy mirrors the growth of medicine itself, advancing in tandem with new discoveries, technologies, and a more profound understanding of human physiology. This journey, however, is not without its challenges. The success of IV therapy hinges not only on its technical proficiency but also on the meticulous attention to detail, unwavering adherence to safety protocols, and the crucial role of healthcare professionals.
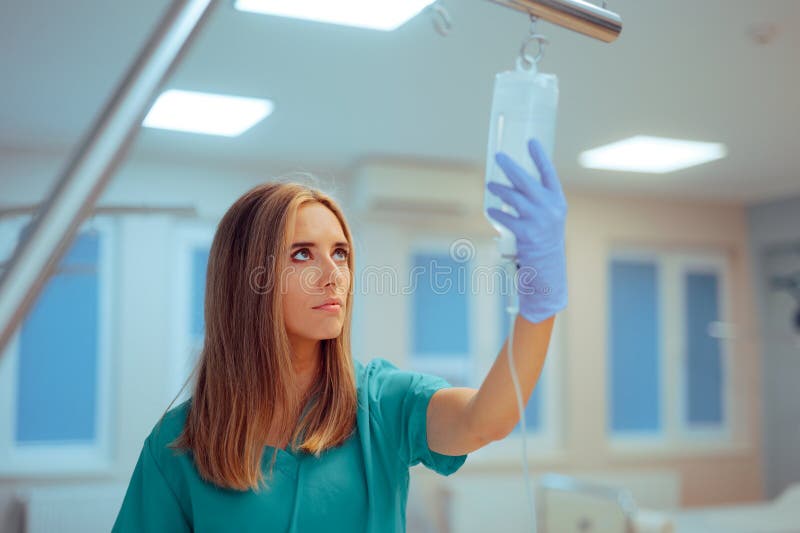
The importance of professional supervision in intravenous therapy is a central theme. A healthcare worker supervising intravenous therapy ensures that the procedure is performed safely and effectively. This oversight is a non-negotiable aspect of providing quality care, reducing the risk of complications, and promoting the best possible patient outcomes. Healthcare professionals administering IV therapy have a significant responsibility, necessitating both a thorough knowledge base and practical skills.
Beyond formal education and licenses, healthcare professionals often require additional certification. This ensures they possess the necessary training and competency in IV therapy techniques. In fact, many healthcare facilities require IV therapy certification as a prerequisite for administering this type of treatment. This emphasis on rigorous training reflects the complexity and potential risks associated with intravenous treatments. The benefits of certification are far-reaching, including improved patient safety, enhanced efficiency, and a commitment to continuous professional development.
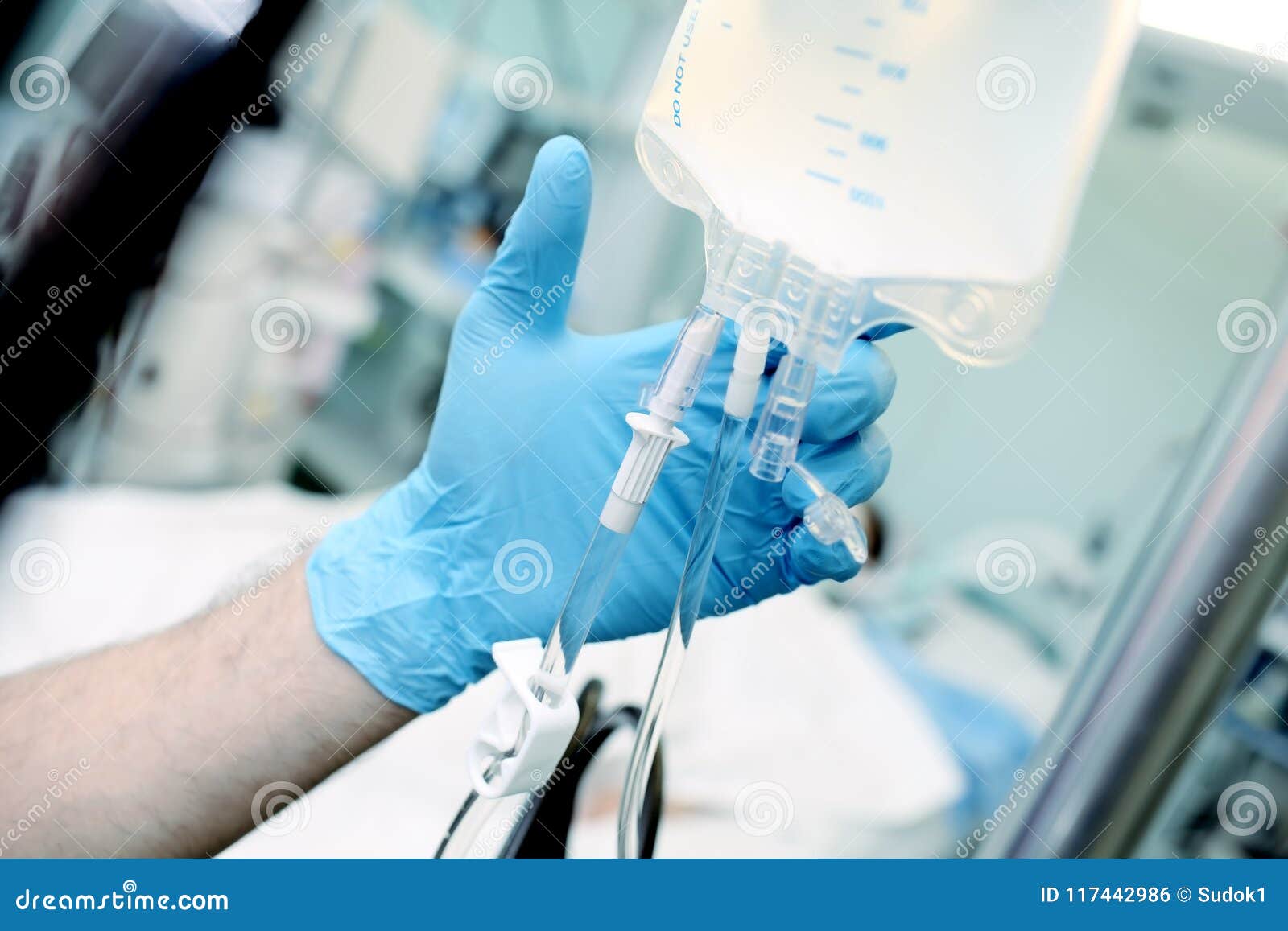
Consider, for example, the critical role of Intravenous (IV) Technicians. IV technicians, often referred to as IV therapy or phlebotomy technicians, are skilled healthcare professionals trained to perform intravenous therapy and related tasks. These duties may involve drawing blood, inserting needles into veins, catheter insertion, IV pump operation, and maintaining the integrity and safety of IV lines. The expertise of these technicians is essential in ensuring the smooth and effective delivery of intravenous treatments. Moreover, in many regions, IV technicians are subject to the requirement of renewing their certification periodically, perhaps through continuing education, ensuring they remain current with the latest best practices.
The image of a dropper for intravenous drug administration, the close-up shots of IV fluids, the details of vaccine administration, and the portraits of patients undergoing IV therapy paint a picture of a field that is both technical and intensely personal. In emergency situations, paramedical personnel can initiate IV therapy, underlining the therapy's importance and accessibility.
In a hospital setting, the process is carefully orchestrated. Physicians order IV therapy, writing specific instructions for the medications to be added to the fluid. Nurses, under these orders, manage the therapy, and the entire system is designed to deliver the most effective care possible. This collaborative approach underscores the need for effective communication, coordination, and a shared commitment to patient safety.
The nurse must also be aware of potential adverse reactions and be prepared to respond accordingly. For instance, should a patient experience complications, such as a change in vital signs, the nurse must immediately slow the IV rate, notify the healthcare provider, and implement measures to ensure the patient's comfort and safety. The nurse should always abide by the health care provider's orders. The results of IV therapy depend primarily on the cause for which the therapy was initiated.
The future of IV therapy in healthcare holds great promise, yet the challenges are equally significant. It is a dynamic field that demands constant attention to safety, efficiency, and innovation. Healthcare providers and facilities can only continue to enhance the quality of patient care if they understand the role of professionals, embrace technological advancements, and maintain a focus on ethical considerations.
The next generation of IV therapy will likely see a shift towards increased patient involvement, remote monitoring, and the utilization of cutting-edge technology to personalize treatment. This evolution will require a skilled workforce and a willingness to adapt. The benefits are clear. Improved patient outcomes, increased efficiency, and enhanced accessibility will reshape healthcare as we know it. This transformative journey is a testament to the unwavering dedication of healthcare professionals and their pursuit of excellence in patient care.
| Area | Details |
|---|---|
| Treatment Type | Intravenous (IV) Therapy |
| Description | Administration of liquid substances directly into a vein for therapeutic purposes. |
| Substances Delivered | Fluids, medications, blood products, nutrients. |
| Key Personnel | Registered Nurses (RNs), IV Technicians, Physicians, Paramedical Personnel (in emergencies). |
| Responsibilities of Supervision | Ensuring safe and effective procedure performance, reducing risks, optimal patient outcomes. |
| Certification Requirements | Often required for healthcare professionals, and renewal may be required through continuing education. |
| Related Tasks | Drawing blood, inserting needles, catheter insertion, IV pump operation. |
| Setting | Hospitals, clinics, and, in emergency situations, pre-hospital environments. |
| Role of Healthcare Professionals | Administer medications and monitor the patient. Also required to recognize adverse reaction symptoms. |
| Importance of healthcare worker | Crucial for maintaining a safe environment for patients, also works under the supervision of a registered nurse and other healthcare professionals, and also provide support to other members of the healthcare team. |
For additional information on IV Therapy, you can consult the following resources:
UpToDate*Note: This link provides comprehensive medical information and is only for informational purposes, and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(882x513:884x515)/Utah-Nurse-Accused-of-Murder-032325-2917df41da574bc599b00b22ee2eb792.jpg)